BECE 2004 Integrated Science Objective Questions and Answers
Answer all questions in this section.
Each question is followed by four options lettered A to D. Find the correct answer for each question.
1. Which of the following processes of conversion of the states of matter is correct?
Solution: Cooling a gas converts it to a liquid (condensation), and further cooling converts the liquid to a solid (freezing). Other sequences violate phase-change principles.
2. The types of energy produced when the hands are vigorously rubbed against each other are
Solution: Friction from rubbing hands generates heat (thermal energy), and the rubbing motion produces audible sound energy. Light/electrical energy isn't typically observed.
3. When a thermometer is put in hot water, the mercury level rises because the mercury increases in
Solution: Mercury expands (volume increases) when heated due to thermal expansion, causing the level to rise. Mass/density/weight remain unchanged.
4. The modes of heat transfer involved in the process of heating water in a bucket from the bottom until it boils are
Solution: Conduction transfers heat from the bottom surface to water molecules. Convection circulates heated water (hot water rises, cool water sinks). Radiation is negligible here.
5. Which of the following items converts chemical energy to electrical energy?
Solution: A dry cell uses chemical reactions (in electrolytes) to generate electrical energy. Bulbs convert electrical→light, loudspeakers/microphones convert electrical↔sound.
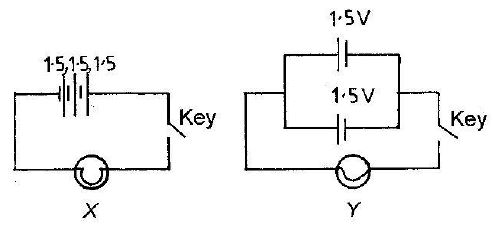
Use the diagrams below to answer Questions 6 and 7
6. Which of the following statements is correct about the circuit diagrams above? The cells in diagram
Solution:Cells in series are connected end-to-end (typical in X). An open key (switch) breaks the circuit. Parallel cells would show side-by-side connections.
7. The total emf of the cells in diagram Y is
Solution: Diagram Y shows two identical cells in parallel. Parallel cells maintain the voltage of a single cell (1.5V), unlike series which add voltages.
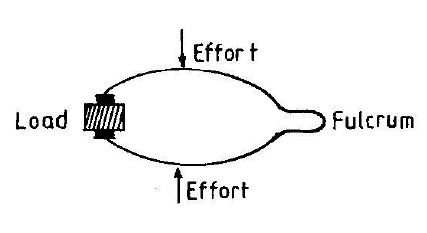
8. It is easier to move a heavy load with a crowbar when the
Solution: Longer effort distance (lever arm) provides mechanical advantage, reducing required force (effort) to move the load per the lever principle \(\text{Effort} \times \text{Effort Arm} = \text{Load} \times \text{Load Arm} \).
9. The type of lever shown above is a
Solution:Third-class levers have effort applied between fulcrum and load (e.g., tweezers, human arm), sacrificing force for speed.
10. A balanced diet is one which is made up of
Solution: A balanced diet requires correct proportions of macronutrients (proteins, carbs, fats/oils), not equal amounts. Water/salt/micronutrients are essential but not defining.
11. Benedict’s solution was added to a mixture in a test tube and it turned brick red when heated. The mixture is likely to contain
Solution: Benedict’s test detects reducing sugars (e.g., glucose). Brick-red precipitate confirms their presence. Oils/proteins/vitamins don’t produce this result.
12. The main food substance present in the albumen of an egg is
Solution: Egg albumen (egg white) is primarily water and proteins (e.g., ovalbumin), with minimal fats/carbs/vitamins.
13. One characteristic which is not common to all living things is the ability to
Solution: All living things grow, respire, and respond to stimuli. "Move about" (locomotion) isn’t universal (e.g., plants, corals).
14. The ovules in a flower develop to form the
Solution: After fertilization, ovules mature into seeds. The ovary (not ovules) develops into fruit.
15. Onions are planted by means of
Solution: Onions grow from bulbs (underground storage organs with fleshy leaves). Corms/suckers/rhizomes are used for plants like taro, bananas, or ginger.
16. The testis in mammals produces
Solution: Testes are male reproductive organs producing sperm and testosterone. Blood/lymph/urine are produced elsewhere.
17. Which of the following structures takes part in human digestion?
Solution: Pancreas secretes digestive enzymes (e.g., amylase, lipase) into the small intestine. Caecum is vestigial, kidneys filter blood, larynx is for speech.
18. Which of the following diseases is contracted through sex?
Solution: HIV/AIDS spreads primarily via sexual contact. Asthma is genetic/environmental, tuberculosis via air, goitre via iodine deficiency.
19. Chlorine gas is an example of
Solution: Chlorine gas (Cl₂) consists of diatomic molecules, but as a pure substance with one type of atom, it’s an element. Compounds have multiple elements.
20. The bad smell that comes out of a urinal is due to the presence of
Solution: Urine breaks down into ammonia (NH₃), which has a pungent odor. Hydrogen/CO₂/nitrogen are odorless.
21. The systematic name of the compound FeS is
Solution: Fe has +2 oxidation state in FeS (since S is -2). Roman numerals indicate metal’s oxidation state: iron(II) sulphide.
22. Which of the following elements is a liquid at room temperature?
Solution: Mercury (Hg) is the only liquid metal at room temperature. Carbon/silver/sulphur are solids.
23. The type of cloud that gives rain is
Solution: "Nimbus" (e.g., nimbostratus, cumulonimbus) denotes rain-producing clouds. Cirrus are wispy, cumulus are fluffy, stratus are layered (non-precipitating).
24. Water drains faster through sand than clay because
Solution: Sand has larger particles and more pore spaces, enabling faster drainage. Clay has tiny particles with less space, retaining water.
25. Which of the following organisms is not an animal parasite?
Solution: Weevils are crop pests (insects) but not parasites—they don’t live on/in hosts. Ticks (ectoparasites), tapeworms/plasmodium (endoparasites) are parasites.
26. The housefly is an agent for the spread of
Solution: Houseflies spread cholera by contaminating food with pathogens from feces. Malaria is spread by mosquitoes; measles/tuberculosis by air/human contact.
27. The best method for checking erosion on a slope is
Solution: Contour ploughing (plowing across slopes) creates ridges that slow water runoff, reducing erosion. Cover cropping/mulching help but are less effective on slopes.
28. It is not advisable to sleep in a closed dark room with green plants because, the plants
Solution: At night (no photosynthesis), plants respire, consuming O₂ and releasing CO₂. In closed rooms, this could reduce oxygen available for humans.
29. The process whereby soil is formed by the breakdown of rocks is called
Solution: Weathering breaks rocks into soil via physical/chemical/biological processes. Erosion transports soil; composting/leaching involve organic matter/nutrient loss.
30. Kerosene is able to reach the other end of a wick by
Solution: Capillary action (movement through narrow tubes via adhesion/cohesion) draws kerosene up the wick. Diffusion/osmosis involve molecules/solvents; suction is pressure-driven.
31. The force, which opposes the motion of one body on another body is called
Solution: Friction opposes relative motion between surfaces. Adhesion/cohesion are attractive forces (different substances/same substance); tension is pulling force.
32. The work done when a force moves a body through a distance of 12 m is 720 J. The force applied is
Solution: Work = Force × Distance → Force = Work/Distance = 720 J / 12 m = 60 N.
33. Food substances are transported from the leaves to various parts of a plant through the
Solution: Phloem transports sugars/organic compounds (food) from leaves. Xylem carries water/minerals; cambium produces cells; epidermis is protective.
34. Which of the following substances are carried by the blood?
I. Nutrients
II. Urine
III. Oxygen
IV. Carbon dioxide
Solution: Blood carries nutrients (I), O₂ (III), and CO₂ (IV). Urine is transported via the urinary system, not blood.
35. A uniform mixture of two or more metals is called
Solution: Alloys are homogeneous mixtures of metals (e.g., brass). Colloids/aerosols are non-metal mixtures; compounds involve chemical bonding.
36. Gold is usually used to make jewellery because it is
Solution: Gold’s low reactivity prevents tarnishing/corrosion, making it ideal for jewelry. Preciousness/expense are secondary; conductivity is irrelevant here.
37. Which of the following substances is a non-metal?
Solution: Diamond is carbon (non-metal). Mercury/sodium are metals; steel is a metal alloy.
38. Alum is added to water during treatment to
Solution: Alum acts as a coagulant, clumping fine particles (flocculation) for easier sedimentation. Disinfection (germ-killing) uses chlorine/UV.
39. Which of the following types of water would be most contaminated by waste substances?
Solution: Streams collect surface runoff (pollutants, waste). Rainwater is purest; borehole/pipe water undergo filtration/treatment.
40. The method of preserving food by drying is similar to salting because in both cases germs are
Solution: Drying/salting remove water (via dehydration/osmosis), creating a hypertonic environment that inhibits microbial growth by preventing metabolism.
1. Question 1
1. (a) Study the simple circuit diagram shown below and answer the questions that follow:
(i) Identify the components labelled I, II, III, IV, V, VI.
(ii) Which component is used to close the circuit?
(iii) State the observation that will be made when the circuit is closed.
(iv) State the energy transformations that take place when the circuit is closed.
(v) Give the name of the circuit connection between components IV, VI.
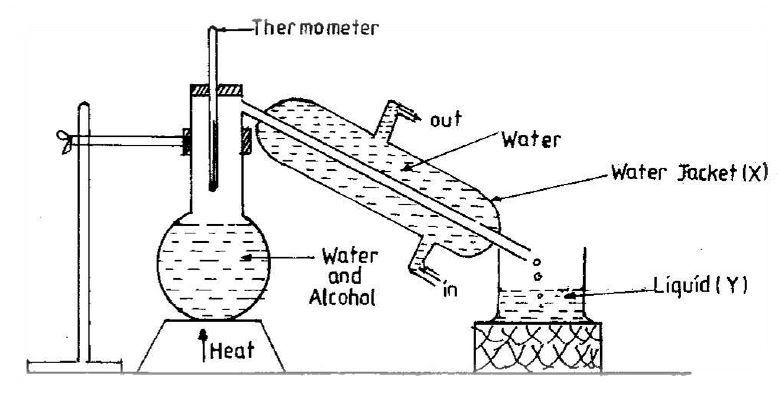
(b) The diagram below is an illustration of an experimental set-up used for separating a mixture of water and alcohol. Study the diagram carefully and answer the questions that follow:
(i) State the method of separation shown in the set-up.
(ii) Identify liquid Y, with reasons.
(iii) Give the functions of the thermometer and the water jacket X.
(iv) What physical processes are involved in the method of separating the mixture?
(v) State the physical property which makes it possible to separate the water and alcohol.
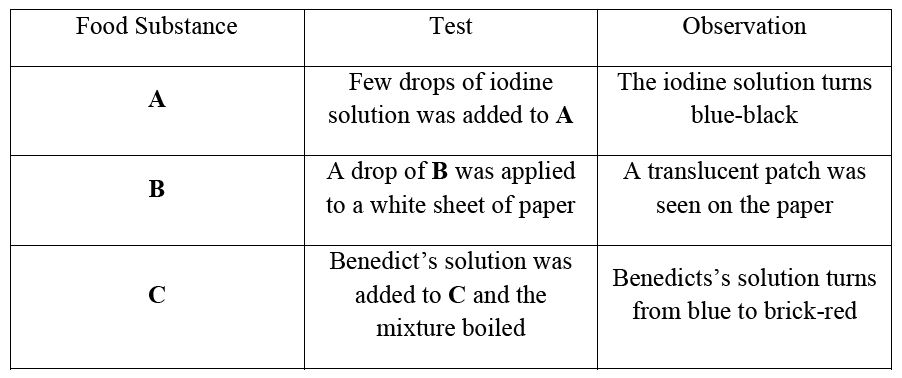
(c) A student performed tests on food substances A, B and C and made the following observations:
| Food Substance | Test | Observation |
(i) Identify food substances A, B and C.
(ii) Give the products of digestion of A, B and C.
(iii) In which parts of the alimentary canal does digestion of each start?
(iv) In which part of the alimentary canal is food substance C absorbed?
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 1
(a) (i) I - Cell, II - Key/Switch, III - Ammeter, IV - Electric bulb, V - Variable resistor, VI - Voltmeter
(ii) The key/switch
(iii) The bulb lights, the ammeter deflects, the voltmeter deflects
(iv) Chemical energy → Electrical energy → Light energy (and heat energy)
(v) Parallel connection
(b) (i) Distillation
(ii) Alcohol – It has a lower boiling point than water, so it vaporizes first.
(iii) Thermometer: Measures temperature in the flask; Water jacket X: Cools vaporized alcohol to condense it back to liquid.
(iv) Vaporization (evaporation) and condensation (cooling)
(v) Difference in boiling points
(c) (i) A - Starch/carbohydrate, B - Fats/oils, C - Reducing sugar/simple sugar
(ii) A - Glucose, B - Fatty acids and glycerol, C - Glucose
(iii) A - Mouth, B - Duodenum (small intestine), C - Mouth
(iv) Ileum (last part of small intestine)
2. Question 2
2. (a) (i) List four parts of a plant that are used for asexual reproduction.
(ii) Give two reasons why sexual reproduction is more advantageous than asexual reproduction.
(b) (i) Explain why atoms are electrically neutral.
(ii) Write the systematic names of:
(α) CuO
(β) SO₂
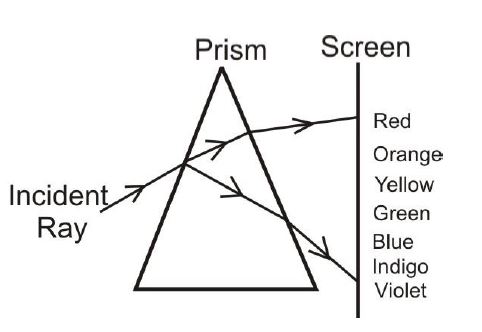
(c) (i) What is dispersion of light?
(ii) Draw and label a diagram of dispersion of light through a triangular glass prism.
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 2
(a) (i) Rhizome, bulb, sucker, stem cutting, tuber, corm, bud
(ii) - Offspring are more resistant to diseases
- Offspring are stronger/healthier
- Offspring have better/diverse characteristics
(b) (i) Atoms have equal numbers of protons (+) and electrons (–), neutralizing charge.
(ii) (α) Copper(II) oxide, (β) Sulfur(IV) oxide
(c) (i) Separation of light into its component colors (wavelengths) when passing through a medium.
(ii) Diagram shows:
- White light entering prism → Refracted into spectrum (VIBGYOR) → Exiting as dispersed light.
Labels: Incident ray, refracted rays, spectrum colors (violet to red).
3. Question 3
3. (a) (i) What is soil erosion?
(ii) Give two types of soil erosion.
(b) Write the name and chemical formula of compounds formed when:
(i) Zinc and oxygen combine
(ii) Calcium and chlorine combine
(c) (i) Distinguish between heat and temperature.
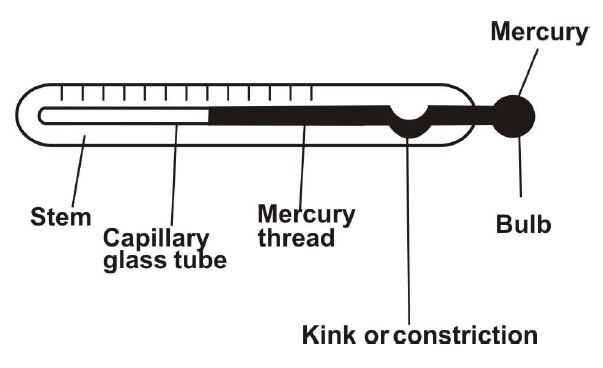
(ii) Draw and label the mercury-in-glass thermometer.
(iii) What mode of heat transfer is involved in using a thermometer?
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 3
(a) (i) Removal of topsoil by natural agents (water, wind, ice).
(ii) Sheet erosion, gully erosion, rill erosion, splash erosion
(b) (i) Zinc oxide (ZnO)
(ii) Calcium chloride (CaCl₂)
(c) (i) Heat: Energy causing hotness/coldness (Joules)
Temperature: Measure of hotness/coldness (°C/K)
(ii) Diagram shows:
-
(iii) Conduction
4. Question 4
4. (a) (i) What is a hormone?
(ii) Copy and complete the table:
(b) Ammonia gas is prepared by heating ammonium chloride and calcium hydroxide.
(i) Write a balanced equation.
(ii) How is ammonia gas tested?
(iii) State one use of ammonia.
(c) (i) Name four types of forces.
(ii) A boy kills a bird on a tree with a catapult. Give two forces involved.
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 4
(a) (i) Chemical secreted by glands to regulate tissue/organ functions.
(ii) 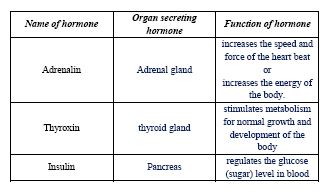
(b) (i) \( \text{NH}_4\text{Cl} + \text{Ca(OH)}_2 \rightarrow \text{NH}_3 + \text{CaCl}_2 + \text{H}_2\text{O} \)
(ii) Pungent smell OR white fumes with HCl.
(iii) Fertilizer production/refrigerant/medicines
(c) (i) Gravitational, frictional, tensional, magnetic, electrostatic, centripetal
(ii) - Tension (catapult elastic)
- Gravity (bird falling)
5. Question 5
5. (a) (i) Distinguish between a rhizome and a stem tuber.
(ii) Give one example each of a rhizome and a stem tuber.
(b) State separation methods for:
(i) Salt and water
(ii) Sawdust and iron filings
(iii) Powdered charcoal and water
(c) (i) Define density.
(ii) Explain how a sinking body can float.
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 5
(a) (i) | Rhizome: Horizontal underground stem, Buds covered by scales,
Stem Tuber: Vertical/diagonal underground stem, Buds (eyes) uncovered
(ii) Rhizome: Ginger; Stem tuber: Potato
(b) (i) Evaporation: Water evaporates, salt remains (different boiling points).
(ii) Magnetization: Magnet attracts iron filings, leaving sawdust.
(iii) Filtration/Decantation: Charcoal is insoluble; filter or pour off water.
(c) (i) Mass per unit volume (\( \text{Density} = \frac{\text{mass}}{\text{volume}} \)).
(ii) Increase volume (e.g., hollow shape) → density decreases below water’s density (1 g/cm³).
6. Question 5
5. (a) (i) Distinguish between a rhizome and a stem tuber.
(ii) Give one example each of a rhizome and a stem tuber.
(b) State the method which could be used to separate each of the following mixtures and explain your answer in each case:
(i) salt and water
(ii) sawdust and iron filings
(iii) powdered charcoal and water
(c) (i) Define density of a substance.
(ii) Explain how a body which sinks in water could be made to float.
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 5
(a) (i) Differences:
- Rhizome grows horizontally below ground; stem tuber grows vertically/diagonally below ground.
- Rhizome has buds covered by scaly leaves; stem tuber has uncovered buds (eyes).
- Rhizome has both nodes and internodes; stem tuber has only nodes.
(ii) Examples:
- Rhizome: Ginger, Canna lily
- Stem tuber: Potato, Yam
(b) Separation methods:
(i) Evaporation:
- Salt dissolves in water but has much higher boiling point. Heating evaporates water, leaving salt crystals.
(ii) Magnetization:
- Iron filings are magnetic; sawdust is non-magnetic. Magnet attracts iron filings, separating from sawdust.
(iii) Filtration/Decantation:
- Charcoal is insoluble in water.
- Filtration: Charcoal trapped by filter paper, water passes through.
- Decantation: After settling, pour water off (if particles settle).
(c) (i) Density definition:
- Mass per unit volume (\( \text{Density} = \frac{\text{mass}}{\text{volume}}\)).
(ii) Floating explanation:
- Increase volume (e.g., hollow shape) → decreases density below water's density (1 g/cm³).
- Result: Upthrust > weight → body floats.